Harddisks, Partitioning, Volumes and Stripe Sets this was tonight’s agenda. Last week we saw how a machine was restored from what was a haddisk partion, but how does a harddisk work, and precisely what is partioning and other things we can do with harddisks.
Below is a diagram of the inside of a harddisk. It isnt recommended you remove the cover from your working harddisks, they are vaccuum sealed, however to get an understanding of the mechanics of one, it might be interesting for you to take apart one from an old computer.

I actually powered up the dismantled drive so that the class could see how it worked. I often refered to how it worked, by drawing parallels to those of a record player, with a stylus and a 12” vinyl record.
We then talked about Disk Formatting and Partitioning. What is Formatting?
Formatting a hard drive is generally done when a new hard drive has been purchased and installed in a new computer. Formatting a hard drive enables it to be able to read and write data by creating a partition on the drive. A hard disk drive can be formatted or reformatted depending on what is being done to the drive
When a new hard drive is formatted a bootable partition is created. The partition that is created is where that operating system is installed. Once a drive has been formatted it can then be used as a Master disk or a Slave disk. A second partition can also be created on the hard drive that can be used as a virtual hard drive.
Formatting a hard drive requires selecting a file system that will be used on the drive. The file system is what the operating system uses to organize and locate information that is written to various sectors on the hard disk. A hard drive with an older files system may not work on a computer designed for a newer file system.
Formatting a hard disk drive will overwrite the data on the drive. However, the data hasn't exactly been erased. The formatting process only removes the operating system's ability to read the data on the drive. Data needs to be rewritten to the drive and then reformatted again to ensure that data is no longer accessible.
Formatting a hard disk drive can fix bad sectors or areas on the disk. When a disk that has errors is reformatted the bad areas of the disk are skipped and not used. This can extend the life of a hard disk drive that can be going bad by isolating the bad areas of the drive.
Useful resources:-
Formatting Disks - Frequently Asked Questions
How to Create and Format a Hard Disk Partition
How to Delete a Hard Disk Partition
Can I repartition my Hard Disk?
We ended the session by discussing what Disk Mirroring, Striping or Extending Volumes and what RAID arrays were. Disk Mirroring is where you have two hard disks fitted into a computer, and when you save data, it is written to both disks. By continuously writing to two sets of disks, you ensure immediate access to duplicate data with virtually no data loss. If one hard drive fails, then the data can be retrieved from the second hard drive.
Disk Striping, in its simplest form is a collection of disks that together, through striping, makes up one unit. So you could have three hard disks in a computer, the first being partitioned as C: and D:, but the D: drive can be extended onto the second and third disks. If each disk were 1 terabyte, you end up with a computer system that has a 500GB C: drive, and a 2.5 TB D: drive.
RAID, an acronym for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a technology that allows high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy. In simpler terms, a RAID array is a grouping of hard drives. A NAS drive for example might have 4 disks in it, but configured in what is known as RAID5 format. The data is written to two drives at a time, allowing at any point one hard disk to physically fail, and the unit to carry on functioning. RAID5 is the most popular, but there are many different configurations.
RAID Level 5 is a cluster-level implementation of data striping with DISTRIBUTED parity for enhanced performance. Clusters can vary in size and are user-definable but they are typically blocks of 64 thousand bytes. The clusters and parity are evenly distributed across multiple hard drives and this provides better performance than using a single drive for parity. Out of an array with “N” number of drives, the total capacity is equal to the sum of “N-1? hard drives. For example, an array with 4 equal sized hard drives will have the combined capacity of 3 hard drives. This is the most common implementation of data striping with parity. In this example 25% of the storage purchased is used for duplication.
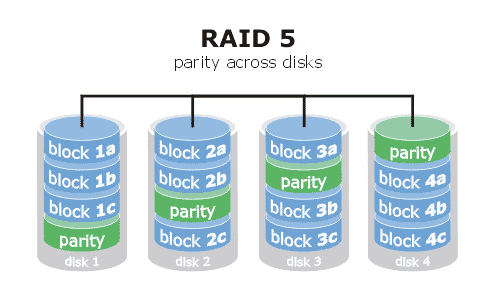
RAID is a good bedtime reading matter, and for further reading at this level here is a good starting point!


 were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products eventually went their separate ways.
were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products eventually went their separate ways.












